In order to extend the service life of the crane, improve the utilization rate of equipment and ensure safe production, must do a good job of routine maintenance of lifting equipment and planned maintenance work.
Do a good job of crane maintenance work during the inspection interval, is to ensure the normal continuous operation of the crane basis. Correctly do the maintenance work during the inspection interval, can extend the inspection interval, reduce the maintenance workload and improve the productivity of the equipment.
Safety Inspection Requirements
Overhead crane and hoists inspections are mandated by both OSHA and ANSI with the various requirements outlined in Federal OSHA 1910.179 regulations as well as various ANSI B30 standards. The types of inspections required in OSHA and ANSI are fairly consistent within the regulation and standards books and include: initial inspection, periodic inspection, frequent inspection, and daily/shift.
“Initial” Inspections: includes a load test of up to 125% of rated capacity and thorough hands-on inspection and operational check of the crane or hoist equipment. The Initial Inspection must be performed when the equipment is installed and whenever repairs are made to critical load-bearing components. The Initial documentation must be maintained for the life of the equipment along with the repair history.
“Periodic” Inspections: include an operational check and thorough hands-on inspection of the crane or hoist equipment. The Periodic Inspection must be performed as frequent as monthly on equipment that has usage that would create the potential for frequent repair and safety issues to as little as annually on seldom-used equipment that has little to no potential for repair and safety issues. The majority of equipment will require quarterly to monthly periodic inspections due to manufacturer requirements and frequency of found defects. Periodic documentation must be also be maintained for the life of the equipment.
“Frequent” Inspections: Include an operation check as well as a visual inspection of critical items listed in the codes and standards such as limit switches, wire rope, chain, hooks, etc. Frequent inspections are required at least monthly and generally done in months when the periodic inspections will not be performed.
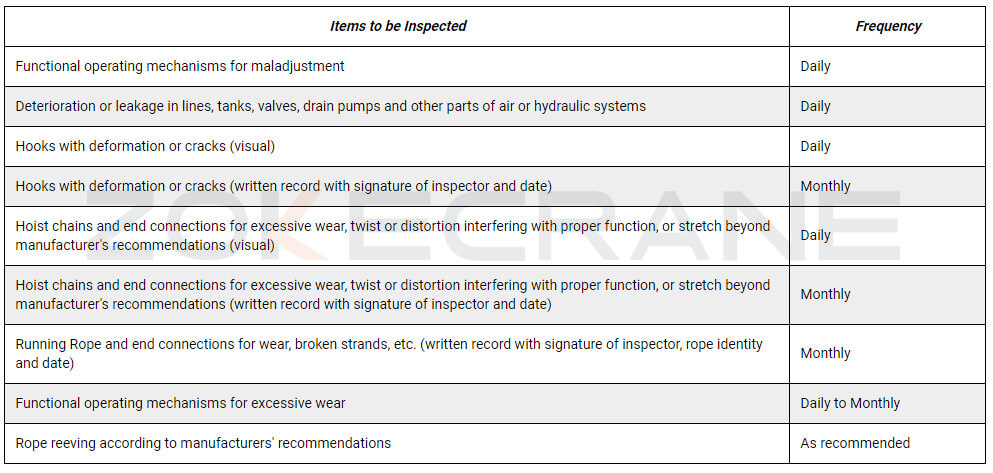
How often should overhead cranes be serviced?

Daily Inspection
This item is combined with the crane operator handover system, mainly by the handover of the crane operator together to check the important electromechanical parts of the crane, such as hooks, wire rope, each agency brake, controller, each agency limiters and various safety switch action is sensitive and reliable. Specific inspection items are as follows.
- Check whether the total power switch of the protection box has been cut off, it is strictly prohibited to check with electricity.
- Whether the wire rope has broken strands and broken wire phenomenon, whether the winding of the reel and pulley is normal, whether there is no groove, knotting, twisting and other phenomena, whether the pressure plate bolt at the end of the wire rope is tight.
- Whether the hook has cracks, whether the hook nut's anti-loose fitting is complete, whether the spreader is complete and reliable.
- Whether the brake tile of each mechanism is close to the brake wheel, the brake tile lining and the brake wheel wear, whether the open position plate is complete, whether the magnet stroke meets the requirements, and whether the rod rotation is stuck.
- The connection bolts of the rotating parts of each institution and the fixed bolts of each component are tight. Whether the wiring of each electrical equipment is normal, and whether the contact between the conductive slider and the sliding line is good.
- The crane check whether the action of the end limit switch is flexible and normal, and whether the action of the safety protection switch is flexible and works normally.
- The rotation of the crane mechanism is normal, there is no abnormal sound.
- And clean the equipment 15 minutes before the end of the shift to maintain a good hygienic environment.
Weekly Inspection
Several operators of the crane will jointly conduct a comprehensive inspection of the crane at the end of each week. The weekly inspection includes:
- Contactor, controller contact contact and corrosion.
- The brake brake friction pad wear.
- The linkage on the key connection and screw tightening.
- The use of more than six months of the wear and tear of the wire rope.
- The lifting mechanism of the double brake, the size of each brake braking torque.
- The electrical limit switch is sensitive and reliable.
Monthly Inspection
Crane operators and maintenance personnel (electrical, clampers) together to check the crane. The content of the monthly inspection includes the following in addition to the content of the weekly inspection.
- The motor, reducer, bearing support, angular bearing box and other base screw fastening and the wear of the motor brush.
- The tightening of the wire rope pressure plate screws, the wear and lubrication of the wire rope used for more than 3 months.
- The wear and tear of the wire insulation layer at the mouth of the pipe.
- The lubrication of each limit switch rotating shaft.
- The amount of lubricating oil in the reducer.
- The wear of steel wire rope at the balance wheel.
- The lubrication of the open gear rotation.
Semi-Annual Inspection
Can be combined with the first level of crane maintenance, operators and repair personnel together. The content of the semi-annual inspection should include the following, in addition to the weekly and monthly inspection.
- The control panel, protection box, controller, resistor and each terminal block, the tightening of the wiring screws.
- The tightening of the end beam screws.
- The brake solenoid cylinder lubrication, hydraulic brake solenoid oil quantity and oil quality.
- The insulation of all electrical equipment.
- Metal structure deformation and the absence of open welding.
- The wheel gnaws the road.
Annual Inspection
In addition to all the content of the half-yearly inspection, should also check the metal components have no cracks, welded seams have no corrosion; size wheel wear condition; measurement of the large car span and large car track span difference; measurement of the static deflection of the main beam and static, dynamic load test; crane for comprehensive lubrication.
Planned Maintenance
Planned maintenance of overhead cranes is the maintenance and repair of cranes within the dates specified in the plan. Its purpose is to prevent excessive wear and tear or accidental damage to the crane, timely elimination of hidden equipment, so that the crane is often in good technical condition, to ensure the safe operation of the crane, to achieve the shortest downtime and minimum maintenance costs to complete the crane maintenance work, so as to achieve the purpose of increasing production and saving, reducing costs. Planned maintenance can be routinely divided into small, medium and large repairs.
Minor Repairs
The task of minor repairs is to remove the faults found in the operation and maintenance of the institution, through the repair and replacement of parts to restore the normal operation of machinery. Minor repair is a partial repair, spending a short time, what is bad to repair what, its maintenance content mainly includes.
- A comprehensive inspection of the entire crane mechanical rotation part, electrical equipment part and metal structure part.
- All lubrication points according to their respective lubrication cycle for cleaning, oil lubrication change.
- Disassembly and inspection, replacement or repair of individual parts.
- Repair or replacement of certain electrical components.
- For the trend of breakage of mechanical and electrical parts, should be prepared for technical work as predictable repair content, in order to deal with the next cycle of repair.
Medium Repair
Medium repair is the partial decomposition of the crane, repair or replacement of worn parts, correction of the geometric position and accuracy of the crane, to maintain the process performance of the crane. Its maintenance content includes, in addition to all the contents of the minor repair, also includes.
- Disassembly and inspection, cleaning, repair or replacement and lubrication of electromechanical components that work frequently and under heavy load.
- The planned replacement of mechanical and electrical components for good technical preparation.
- A comprehensive inspection of the crane electrical wiring, replace part of the aging wiring and broken electrical components.
Large Repairs
large repairs is all disassembly, disassembly and inspection of each component, repair repairable parts, replacement of non-repairable parts or individual components, cranes are required to achieve or close to the technical standards and mechanical properties specified in the factory after overhaul. Its maintenance content mainly includes.
- Institutional part of all the agencies decomposition, including reducers, couplings, reel groups, wheel groups and pick-up devices and other components, replacement of damaged and scrap standard parts, cleaning and reassembly and oil lubrication, replacement of wire rope, each agency brake and its open mount.
- The motor of each institution should be dispersed, dried, assembled and oiled and lubricated, and the severely damaged motor should be replaced. Replace the opening device of each mechanism brake; replace the broken cam controller of each mechanism; overhaul the protection cabinet or replace the protection cabinet; replace the wiring of all the lines and re-wire the installation; replace the control board of the lighting signal system, etc.
- Metal structure part, the main beam has been deflected or side bending to correct the repair and reinforcement; the whole crane all clean and paint 2 times to protect.
- After overhaul, the crane should be debugged, and then identified according to the static and dynamic load test procedure, and only after passing can be put into production use.
Common Problems with Overhead Cranes:
1. Damage or Degradation to the Wire Rope

Birdcaging, corrosion, abrasion, and extreme wear are a few of the problems that can affect wire rope on an overhead crane. The best way to prevent damage or failure is to inspect your wire rope regularly.
Damage or degradation to wire rope is one of the most common issues that you may experience with an overhead crane system. There are a number of common wire rope problems, including any of the following:
- The wire rope has jumped out of the reeving system
- Reduction of rope diameter below nominal – loss of core support, internal or external corrosion, wear of outside wires
- Broken or worn outside wires
- Corroded or broken wires at end connections
Many operating conditions can affect the life of wire rope. Bending, stresses, loading conditions, speed of load application (shock load), abrasion, corrosion, sling design, materials handled, environmental conditions (heat or chemical exposure), lubrication, and history of usage will all factor into how long wire rope can stay in service.
The best way to prevent damage to, or failure of, a wire rope is to inspect it prior to each shift. If any evidence of damage is observed, the wire rope should be properly disposed of to prevent further usage.
Also, make sure that the wire rope is properly lubricated. Proper lubrication of the wire rope has two primary benefits:
- Reduces friction as the individual wires move over each other
- Provides corrosion protection and lubrication in the core, inside wires, and outside surface
2. Excessive Wear to End Truck Wheels
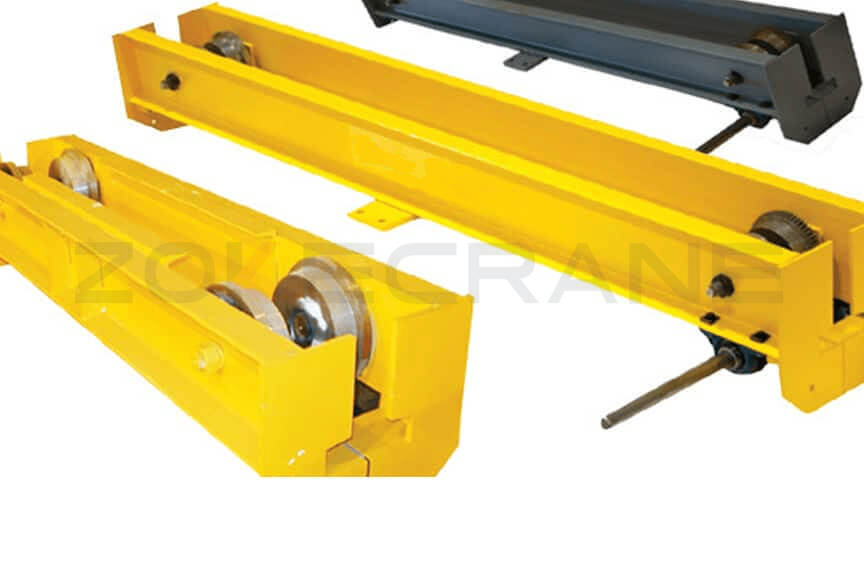

A runway system that isn't properly aligned can cause premature wear to the crane's end trucks and wheels, motor drives, and other equipment.
End truck wheels are components of overhead cranes that can require frequent maintenance, replacement, or adjustment. Throughout the course of a crane's life, the wheels will naturally wear down due to normal use of the crane and will need to be replaced.
Wheels can be made of a variety of materials, including polyurethane for gantry cranes, alloys, low-carbon steel, or medium-carbon steel. The more carbon in the steel, the harder the wheel will be. There are also methods of heat-treating that can be used to increase the hardness of a wheel—increasing the service life and load capacity of the wheels.
If the wheels, wheel bearings, or wheel flanges begin to wear or break down prematurely, it can be an indication that the crane is skewing and not properly tracking down the runway system. Skewing of the crane can cause excessive wear and stress on the wheels, but also on the runway beams and support structures as well.
Wheels tend to wear out faster on a crane that was installed using an existing rail system as opposed to a new installation. Unless the runway has been properly surveyed prior to installation, the runways may be misaligned or the rails may be out of tolerance.
To avoid premature wear on the wheels and end trucks, your overhead crane runway system should be designed, tested, and regularly inspected by a reputable overhead crane manufacturer. Any signs of premature wear will indicate the possibility of a larger problem that should be addressed and corrected before the problem compounds itself. Make sure wheels were made specifically for the rail they're running on. Hardness must match hardness of rail.
3. Issues with The Electrification System
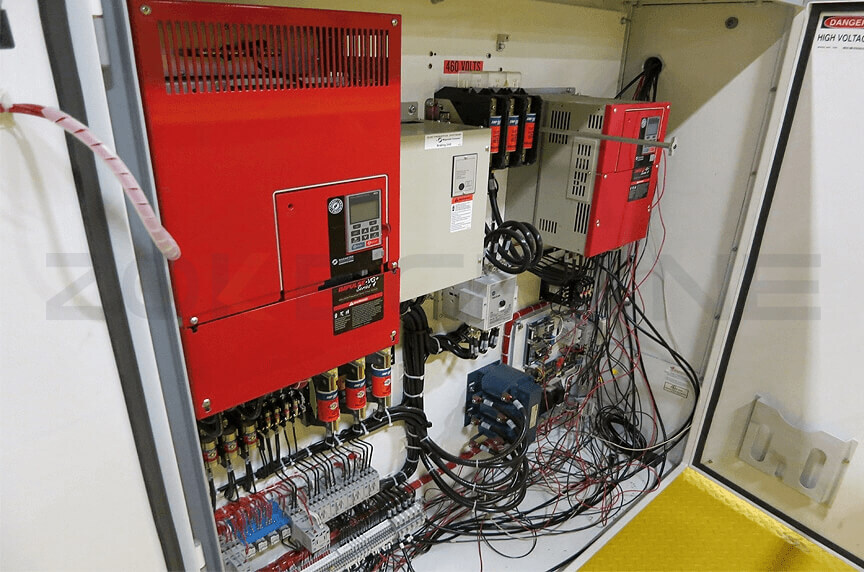

If your overhead crane is blowing fuses, then you may have a faulty circuit in the crane's electrification system. Contact a crane service provider immediately to come out and identify the fault.
There are a number of different issues related to an overhead crane's electrification system that may require service or future maintenance.
Problems with Contact Interruptions
One of the most frustrating problems that a crane operator can experience is when there are contact interruptions between the conductor bars and the collector. These contact interruptions can cause intermittent control problems with the overhead crane system.
On the collector, a brush made from carbon graphite can wear down, which can cause carbon graphite to build up. Because carbon graphite dust is a conductive material, this build up can cause shorts in the electrical connection.
On older crane systems, the copper rails on the conductor bars can also become corroded or oxidized due to the operating environment or due to long periods where the crane is not being used. To prevent this from happening, the conductor bars and collectors should be inspected and cleaned regularly to make sure that the contact between the collector and conductor bar is uninterrupted.
Another problem that can cause contact interruptions is if there are alignment issues with the conductor bars themselves, causing the collector shoes to jump out of the track and lose contact.
Problems with Push Button Pendants or Radio Controls
Although not very common, there are environments that create their own radio waves that may interfere with the operation of an overhead crane. An example might be a facility that performs induction heating or induction welding procedures.
Radio waves created during these processes may disrupt the communication between the radio's transmitter and receiver.
On pendant controls and radio controls, the push buttons or levers may stick or become unresponsive over time. The control may need to be replaced or repaired to correct any issues with the operation of the buttons.
You may also find that pendant controls can become disconnected or pulled out of the hoist. The reason that this can occur is because the operator pulls on the pendant to maneuver or position the crane—especially on jib cranes or workstation cranes. If your controls become unresponsive, you may need to check to see if the pendant became disconnected from the hoist, or have the system serviced and re-wired if any wires become loose.
Blown Fuses
If you find that your overhead crane is blowing fuses, then it's an indication that you have a faulty circuit in the crane's electrification system. Contact a crane service provider immediately to come out and inspect the crane's electrification system and identify the fault.
4. Bent or Damaged Hooks
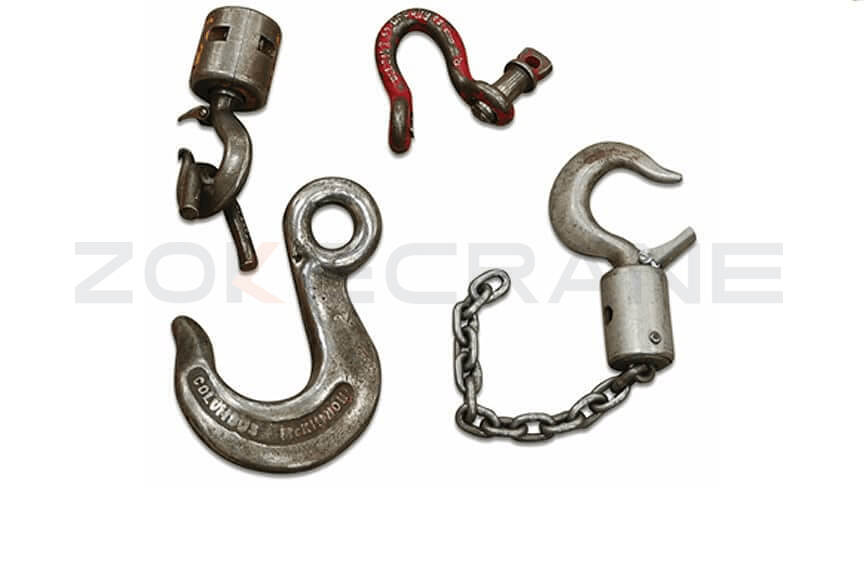

Regular inspection of hooks and other pieces of rigging hardware should be performed at the beginning of each shift to check for deformities or damage.
A hook is designed to hold a load in a particular and precise direction. When the weight isn't supported as intended by the hook, it compromises the internal integrity of the hook and can increase the chance of it bending, stretching, or cracking. The load can also slip off of the hook if it stretches out the throat opening.
Regular inspection of hooks and other pieces of rigging hardware should be performed at the beginning of each shift to check for deformities or damage.
While there are no clear-cut guidelines on the use of hook latches, we train our employees and inspectors that if a hook is designed to have a latch, it should have the latch installed to help move a load safely and securely. We advise that the end user must evaluate the work activity with regards to the safety of their employees. If the activity makes the use of the latch impractical, unnecessary, or more dangerous, then the end user may choose to eliminate the latch. It is also recommended that each lifting activity is considered independently as far as the use of a hook latch is concerned.































